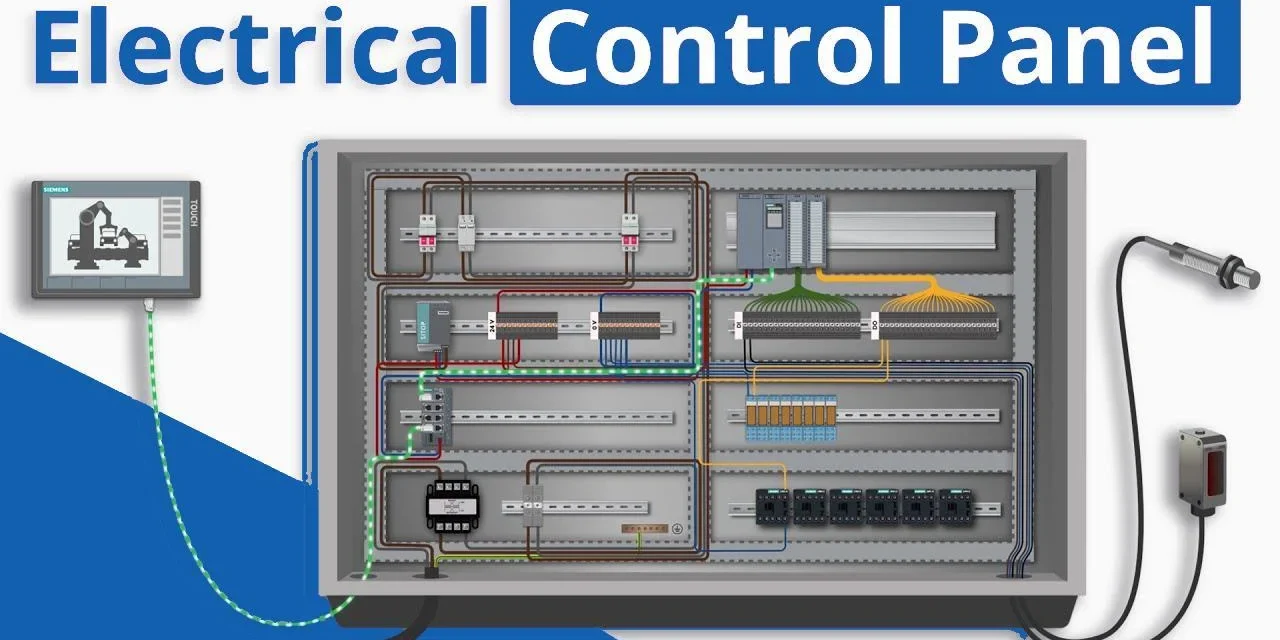
Maintaining and ensuring the safety of control panels and their components is crucial for reliable operation, preventing failures, and minimizing the risk of electrical hazards. A well-maintained control panel can extend the lifespan of components, reduce downtime, and ensure compliance with safety standards. Below are the key practices for maintaining and ensuring the safety of control panels and their components:
1. Regular Inspection and Visual Checks
- Purpose: To identify any potential issues, such as damaged wiring, loose connections, or signs of wear.
- Action: Inspect the control panel regularly for:
- Loose or corroded connections: Ensure all terminals, screws, and connectors are tight and corrosion-free.
- Overheating signs: Look for discoloration, burn marks, or melted insulation that could indicate overheating.
- Dust and debris: Dust accumulation can lead to short circuits or reduced cooling efficiency.
- Physical damage: Check for broken or damaged components such as fuses, relays, and switches.
2. Cleaning and Dust Removal
- Purpose: Dust and dirt can cause overheating and electrical faults.
- Action:
- Use compressed air to blow out dust from components such as relays, transformers, and circuit breakers.
- Ensure that the control panel is cleaned without using excessive moisture, which could cause short circuits.
- Use soft brushes to remove dirt from delicate components.
- Ensure that air vents or cooling fans are not obstructed by dust, as this can lead to overheating.
3. Tightening and Re-tightening Connections
- Purpose: Loose connections can cause arcing, overheating, and equipment failure.
- Action:
- Periodically check and tighten all electrical connections, especially for high-power connections like circuit breakers, busbars, and terminals.
- Use a torque wrench to ensure that connections are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
4. Checking and Testing Circuit Breakers and Fuses
- Purpose: Circuit breakers and fuses protect the control panel from electrical overloads and short circuits.
- Action:
- Test circuit breakers and fuses periodically to ensure they trip and protect the system effectively.
- Replace any faulty or worn-out breakers and fuses immediately.
- Ensure that breakers are rated correctly for the expected load.
5. Regular Calibration of Meters and Sensors
- Purpose: To ensure accurate readings for parameters like voltage, current, temperature, or pressure.
- Action:
- Calibrate meters, voltage sensors, and other monitoring devices regularly as per the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Ensure that the readings provided by meters are within the allowable tolerance.
6. Monitoring and Preventing Overheating
- Purpose: Overheating can lead to component failure, fires, or electrical hazards.
- Action:
- Monitor the temperature inside the control panel with temperature sensors.
- Ensure that cooling systems, like fans and air conditioning units, are functioning properly.
- Avoid placing control panels in areas with excessive heat or poor ventilation.
7. Testing and Verifying Safety Systems
- Purpose: Safety systems, such as emergency stop switches, alarms, and protective relays, must function correctly to prevent accidents.
- Action:
- Periodically test emergency stop buttons, safety relays, and alarms to verify they function as intended.
- Check protective relays for correct settings, calibration, and response times.
- Verify that grounding and earthing systems are intact to ensure operator safety.
8. Preventing Moisture and Humidity Issues
- Purpose: Moisture can cause corrosion, short circuits, and reduced equipment lifespan.
- Action:
- Install moisture-detecting sensors or dehumidifiers in control panels located in high-humidity environments.
- Ensure that enclosures are properly sealed and protected from water ingress, especially if the panel is located outdoors or in damp environments.
9. Ensuring Proper Ventilation
- Purpose: Adequate ventilation helps to prevent overheating and ensures the longevity of components.
- Action:
- Verify that ventilation openings, cooling fans, and exhaust systems are free from obstruction.
- Use fans or air conditioners if necessary to maintain a stable internal temperature in the control panel.
10. Conducting Functional Testing
- Purpose: Ensure that the control system operates as intended and that all components respond to input signals.
- Action:
- Perform functional testing to ensure the PLC or control system operates correctly.
- Verify that relays, contactors, and switches activate and deactivate as expected.
- Test the response times of safety systems and alarms.
11. Performing Electrical Insulation Resistance Tests
- Purpose: To check for insulation degradation, which can lead to electrical short circuits or failures.
- Action:
- Use insulation resistance testers to test the condition of the panel’s wiring insulation.
- Ensure that the resistance is within acceptable limits and replace any faulty cables or insulation.
12. Software and Firmware Updates (for PLCs and HMIs)
- Purpose: Software or firmware bugs can cause the control system to malfunction, leading to safety issues or inefficiency.
- Action:
- Periodically check and update the software or firmware of PLCs, HMIs, and other programmable systems to the latest versions provided by manufacturers.
- Ensure that any security patches or critical fixes are applied to avoid cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
13. Keeping Documentation Up to Date
- Purpose: Proper documentation ensures that maintenance personnel can quickly understand the system and respond to issues effectively.
- Action:
- Maintain accurate records of all maintenance activities, including component replacements, inspections, and tests.
- Ensure that wiring diagrams, component manuals, and schematics are kept up to date.
14. Emergency Preparedness and Response
- Purpose: In case of a failure, there should be a well-defined plan to address the issue swiftly and safely.
- Action:
- Provide proper training to operators and maintenance personnel on emergency procedures.
- Ensure the availability of emergency stop buttons and easily accessible shutdown procedures.
- Create and practice contingency plans for electrical failures, fires, or faults.
15. Compliance with Standards and Regulations
- Purpose: Compliance with local and international safety standards ensures the safety of personnel and equipment.
- Action:
- Follow applicable standards like IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), NFPA (National Fire Protection Association), and OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) guidelines.
- Ensure that control panels are installed and maintained according to regulatory codes and standards.
The safety and reliability of control panels can be significantly enhanced through regular maintenance, proper inspections, and adherence to safety standards. It is essential to monitor critical components, test safety systems, and maintain clear documentation to prevent operational failures and protect personnel from hazards.