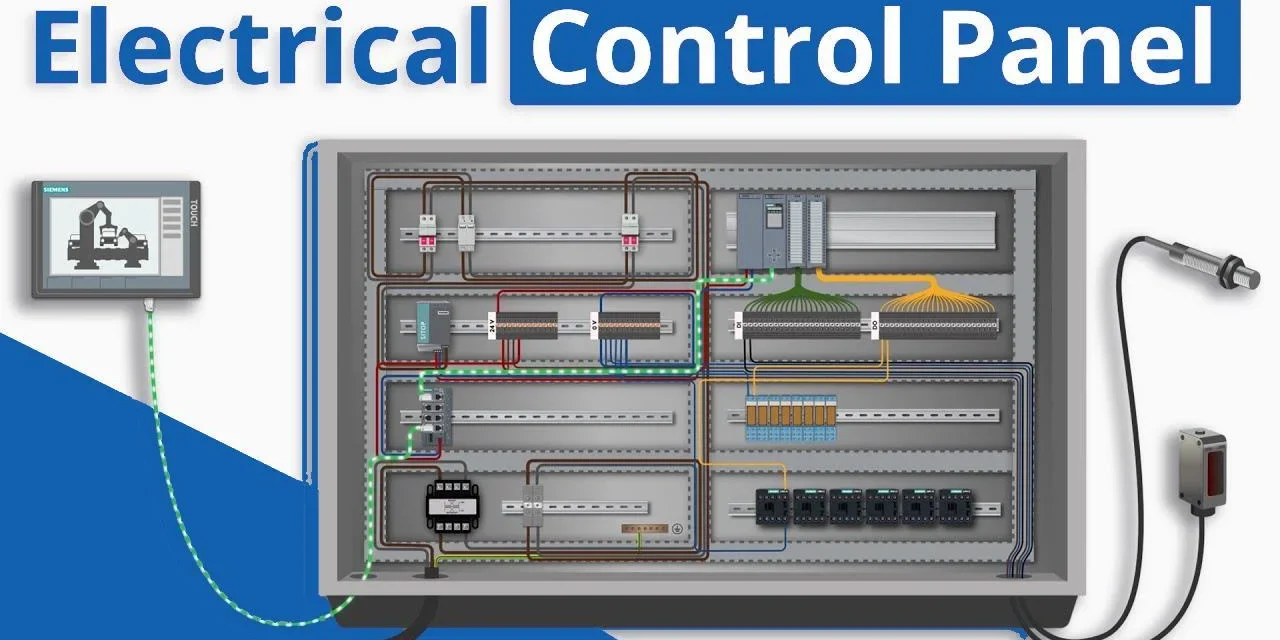
1. Circuit Breakers and Fuses
- Purpose: These protective devices interrupt the electrical flow in case of overloads, short circuits, or other faults, preventing damage to the system and ensuring safety.
- Function: Circuit breakers automatically disconnect the electrical circuit when faults occur, while fuses perform a similar function but need to be replaced once blown.
- Types: Thermal, magnetic, and combination circuit breakers.
2. Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
- Purpose: The PLC is the brain of the control panel, providing the logic and processing power to control the system. It executes programmed instructions based on input signals and determines the outputs.
- Function: It automates processes, manages signals from sensors, and sends commands to actuators and other devices.
- Types: Compact PLCs, modular PLCs, and rack-mounted PLCs.
3. Relays and Contactors
- Purpose: Relays and contactors are electromagnetic devices used to switch electrical circuits on and off, typically in response to signals from the PLC or other control systems.
- Function: Relays are used for low-power applications, while contactors are designed for high-power switching, such as motor control.
- Types: Electromechanical and solid-state relays.
4. Switches
- Purpose: Switches allow the operator to manually control the electrical system, turning it on or off as needed.
- Function: Push-button switches, toggle switches, and selector switches are used for operational control by the user.
- Types: Push buttons, selector switches, emergency stop switches, and lighted indicators.
5. Meters
- Purpose: Meters are used to measure various electrical parameters such as voltage, current, frequency, power, and energy consumption. These measurements help monitor and optimize the system.
- Function: Digital and analog meters provide real-time feedback to operators, ensuring the system is operating within the specified limits.
- Types: Voltmeters, ammeters, wattmeters, power meters, and frequency meters.
6. Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
- Purpose: The HMI provides a user-friendly interface for operators to interact with the control panel and monitor or control the system.
- Function: It displays real-time data, allows input from the operator, and shows alarms, warnings, and system status.
- Types: Touchscreen HMIs, LED/LCD displays, and graphical interfaces.
7. Busbars
- Purpose: Busbars are metallic conductors used to distribute electrical power within the control panel to various components or systems.
- Function: They allow for efficient power distribution and facilitate the connection of circuit breakers, fuses, and other electrical components.
- Types: Copper busbars, aluminum busbars, and insulated busbars.
8. Terminal Blocks
- Purpose: Terminal blocks are used to connect wiring from the electrical devices to the control panel in an organized manner.
- Function: They simplify the wiring process and provide a safe, secure, and easily accessible point for making electrical connections.
- Types: Screw-type, spring-type, and modular terminal blocks.
9. Transformers
- Purpose: Transformers are used to change the voltage level in the control panel, either stepping it up or down to match the requirements of various components or external systems.
- Function: They allow the control panel to operate at different voltage levels while ensuring safe operation of components.
- Types: Step-down transformers (for voltage reduction) and isolation transformers (for safety).
10. Power Supply Units (PSUs)
- Purpose: Power supply units provide the necessary voltage and current for the control panel’s components, particularly the PLC, relays, and other low-voltage devices.
- Function: They convert incoming AC or DC power into the required operating voltage.
- Types: AC-DC power supplies, DC-DC converters, and battery-backed power supplies.
11. Sensors
- Purpose: Sensors provide input signals to the control panel, detecting physical variables such as temperature, pressure, level, flow, or humidity.
- Function: They enable the control system to monitor and respond to changes in the environment or system conditions.
- Types: Proximity sensors, temperature sensors, pressure sensors, and flow sensors.
12. Actuators
- Purpose: Actuators are devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical movement to perform tasks such as opening or closing valves, moving motors, or adjusting positions.
- Function: They carry out actions in response to signals from the PLC or control system, often based on sensor inputs.
- Types: Electric motors, solenoids, pneumatic actuators, and hydraulic actuators.
13. Alarm Systems and Indicators
- Purpose: Alarm systems are used to alert operators to faults, system failures, or safety hazards.
- Function: Alarms can be visual (flashing lights, LED indicators) or audible (buzzers, horns) to indicate that attention is required.
- Types: Audible alarms, visual indicators, and combined alarm systems.
14. Enclosures and Mounting Systems
- Purpose: The enclosure houses and protects the components of the control panel from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and physical damage.
- Function: It provides safety for operators and ensures that the system is stable and secure.
- Types: Metal enclosures (steel, aluminum), plastic enclosures, and weatherproof enclosures for outdoor use.
15. Grounding and Safety Components
- Purpose: Grounding components are used to ensure the electrical safety of the control panel by preventing electrical shocks or short circuits.
- Function: They connect the panel to the earth and provide a path for fault currents to safely dissipate.
- Types: Grounding bars, earthing conductors, and surge protection devices.
16. Wiring and Cables
- Purpose: Wiring and cables are used to connect the various components within the control panel and to external systems.
- Function: They carry the electrical signals and power to ensure the proper operation of the system.
- Types: Control cables, power cables, signal cables, and fiber-optic cables.
Control panels are made up of a wide variety of components that are designed to ensure the effective operation, protection, and safety of electrical systems. Each component plays a critical role in ensuring that the system operates efficiently and safely, and that operators can control and monitor the system with ease. The selection of components depends on the complexity of the application, the required functionality, and the specific industry requirements.