Electrical devices play a crucial role in the electronics and electrical equipment industry, serving as the essential components that power, control, and support various systems and applications. These devices are fundamental to the operation of everything from household electronics to industrial machinery, infrastructure, and communication systems. The function of electrical devices can be broken down into several key categories, each serving a specific role in the industry:
1. Power Generation and Distribution
- Power Generation Equipment: Devices like generators, turbines, and solar panels are responsible for converting different types of energy (mechanical, thermal, solar) into electrical energy. These devices are critical for providing electricity in homes, industries, and infrastructure.
- Transformers: Transformers step up or step down the voltage in electrical circuits, enabling the efficient transmission and distribution of electricity over long distances. Without transformers, power loss would be high, and efficient distribution would be impossible.
- Circuit Breakers and Fuses: These devices protect electrical systems by interrupting the flow of electricity in case of faults or overloads. They prevent damage to wiring and electrical devices by cutting off power when needed.
2. Control and Automation
- Switches and Relays: Switches are devices that open or close electrical circuits, allowing current to flow or be interrupted. Relays, on the other hand, are electrically operated switches used to control high-power circuits with low-power signals. They are widely used in automation, allowing systems to be controlled remotely or automatically.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): PLCs are industrial digital computers used for automation of electromechanical processes. They control manufacturing processes, machinery on production lines, or other automated systems.
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): VFDs control the speed of electric motors by varying the frequency of the power supplied to the motor. They are crucial for energy savings, speed control, and precise operation in industrial equipment.
3. Signal Processing and Communication
- Amplifiers: Amplifiers increase the amplitude of electrical signals. They are used in audio systems, telecommunications, broadcasting, and other applications that require signal enhancement.
- Transmitters and Receivers: These devices are used for wireless communication. Transmitters convert information into electrical signals and send them through various mediums (e.g., radio waves, fiber optics), while receivers capture and decode the transmitted signals.
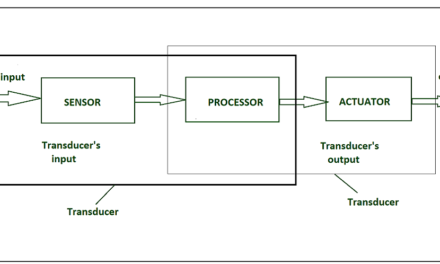
- Sensors: Electrical sensors detect physical phenomena (e.g., temperature, pressure, motion) and convert them into electrical signals that can be read, processed, or acted upon by other devices. They are widely used in applications ranging from automated manufacturing to smart homes and healthcare devices.
4. Power Conversion and Regulation
- Rectifiers: Rectifiers convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). This is important for supplying power to electronic devices like computers, mobile phones, and other DC-powered systems.
- Inverters: Inverters convert DC to AC, which is necessary for devices that operate on AC power, such as inverters used in solar power systems, motor drives, and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
- Voltage Regulators: These devices ensure a consistent output voltage level to electrical devices, protecting them from voltage fluctuations that could cause damage or erratic behavior. Voltage regulators are essential in stabilizing power supplies to sensitive electronics.
5. Energy Storage
- Batteries: Batteries store electrical energy chemically and are used in devices ranging from smartphones to electric vehicles. The development of higher-capacity, longer-lasting, and faster-charging batteries has been essential in powering portable and mobile electronic devices.
- Capacitors: Capacitors store electrical energy temporarily and release it when needed. They are commonly used to smooth out voltage fluctuations in power supplies and can also be found in timing circuits and memory storage applications.
6. Measurement and Testing
- Multimeters: These devices measure electrical parameters like voltage, current, and resistance. They are essential for troubleshooting, maintaining, and testing electrical and electronic equipment.
- Oscilloscopes: Oscilloscopes visualize electrical signals over time, allowing engineers to analyze waveforms, frequency, and amplitude. They are used extensively in research, development, and repair of electronic systems.
- Power Meters: These devices measure electrical power consumption, providing data on the efficiency and energy use of electrical systems. They are important in both consumer and industrial applications to monitor and manage energy consumption.
7. Consumer Electronics and Appliances
- Smartphones, Laptops, and Tablets: These devices rely on a variety of semiconductors, sensors, power management circuits, and other electrical components to function. Electrical devices in these gadgets support data processing, communication, and power management.
- Home Appliances: Appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners use electrical devices like motors, heaters, compressors, and controllers to perform their functions. Energy-efficient devices with advanced smart technologies are becoming increasingly common.
- Audio and Visual Devices: Devices such as TVs, sound systems, and cameras incorporate amplifiers, signal processors, sensors, and displays, all of which rely on electrical components to deliver high-quality audio-visual experiences.
8. Lighting and Displays
- LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes): LEDs are widely used in displays, lighting, and signaling. They offer energy efficiency, long lifespan, and compact design. In the electronics industry, LEDs are used in everything from TVs and smartphones to automotive lighting and indoor lighting systems.
- LCDs (Liquid Crystal Displays): LCDs are used in a variety of display applications, including smartphones, TVs, and computer monitors. They require electrical components like inverters, backlight units, and control circuits.
- OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diodes): OLEDs offer improved picture quality, flexibility, and power efficiency. They are commonly used in high-end displays, such as smartphones and TVs.
9. Electrical Safety and Protection
- Surge Protectors: Surge protectors are designed to protect sensitive electronic devices from voltage spikes caused by power surges or lightning strikes. They typically incorporate fuses and clamps to prevent damage to electrical devices.
- Grounding Systems: Grounding is used to prevent electrical shock by directing any stray current safely into the ground. Proper grounding is essential for electrical safety in homes, buildings, and industrial systems.
- UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supplies): UPS systems provide backup power in case of an electrical outage. They typically contain batteries that keep critical equipment running during power failures, such as in hospitals, data centers, and industrial environments.
10. Telecommunications Equipment
- Switches and Routers: Used in network communication to direct data traffic and ensure reliable data transmission. These devices rely on semiconductors and integrated circuits to process, route, and forward data packets between networks.
- Modems: Modems modulate and demodulate digital signals, allowing for communication between different types of networks (e.g., broadband, wireless, cable, or fiber optics).
- Antennas: Antennas are used to send and receive electromagnetic signals for wireless communication systems, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 5G, and satellite communication.
Conclusion
Electrical devices serve a vast range of functions within the electronics and electrical equipment industry, spanning power generation, signal processing, automation, energy storage, and consumer electronics. These devices are fundamental to the proper operation of electrical systems and electronic devices, allowing for efficient, safe, and sustainable power usage, advanced communication, and intelligent control. As technology advances, the role of electrical devices will continue to evolve, driving new innovations and creating opportunities across diverse industries.
Hashtags
#PowerSupply #ElectricalDistribution #EnergyManagement #PowerConversion #PowerGeneration #ElectricalPower #PowerControl #SignalProcessing #ControlSystems #SignalAmplifiers #SignalConversion #ElectronicControl #AnalogToDigital #SignalTransmission #PowerManagement #EnergyStorage #BatteryTech #PowerRegulation #EnergyStorageSystems #EnergyHarvesting #PowerEfficiency #CircuitProtection #ElectricalSafety #SurgeProtection #OverloadProtection #FuseAndBreaker #SafetyDevices #ElectricalRiskManagement #LightingDevices #LEDLighting #SmartLighting #EnergyEfficientLighting #LightingControl #LightingSolutions #IlluminationTech #Sensors #MeasurementDevices #SmartSensors #CurrentSensors #VoltageSensors #PowerMeters #EnvironmentalSensors #SwitchingDevices #ElectricalSwitches #AutomationControl