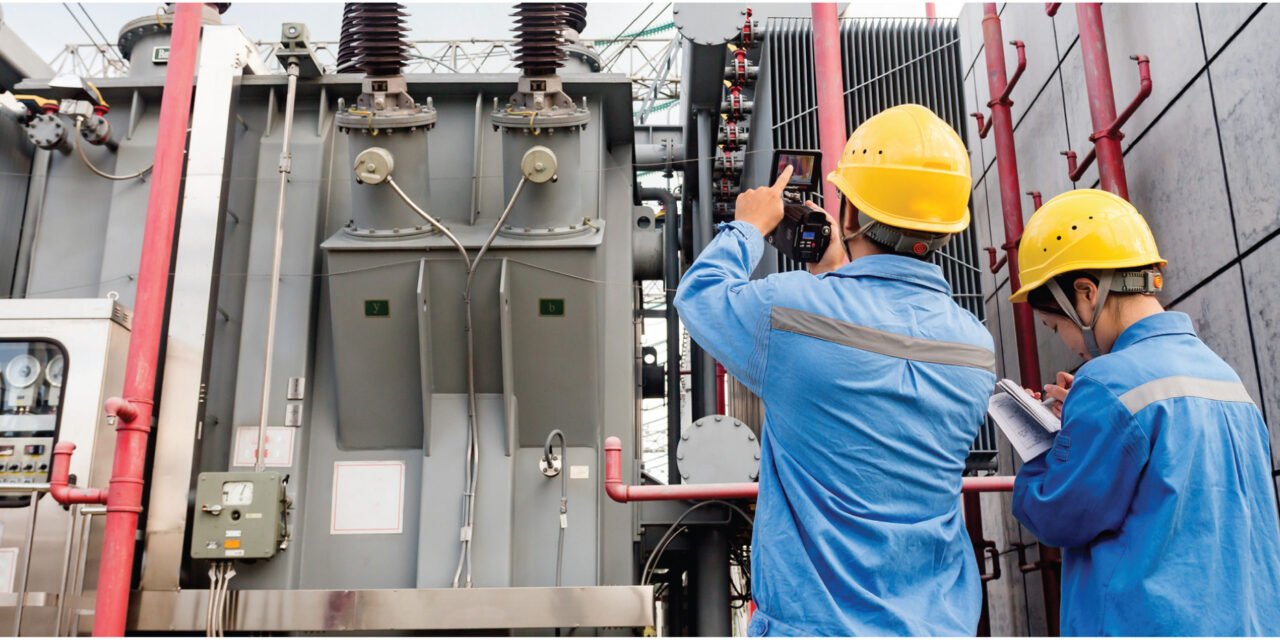
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the reliable and efficient operation of transformers and electrical devices, prevent failures, and extend their lifespan. Maintenance practices typically include inspections, testing, cleaning, and repairs. Below is a comprehensive guide to key maintenance practices for transformers and electrical devices:
Maintenance Practices for Transformers
1. Visual Inspection
- Frequency: Monthly or as needed.
- What to Check:
- Leaks in oil-filled transformers.
- Physical damage to the tank, bushings, or cooling fins.
- Cleanliness of insulators and bushings to prevent tracking and arcing.
- Signs of overheating, corrosion, or unusual noise.
2. Oil Analysis (For Oil-Filled Transformers)
- Frequency: Annually or as required.
- Tests:
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA): Detects gases generated by insulation and oil degradation, which can indicate overheating or arcing.
- Moisture Content: High moisture reduces insulation strength.
- Acidity (TAN): Measures oil degradation levels.
- Dielectric Strength: Tests the insulating properties of the oil.
3. Thermal Imaging
- Frequency: Annually or during load checks.
- Purpose:
- Identify hot spots or uneven temperature distributions.
- Detect early signs of overheating or failing components.
4. Electrical Testing
- Frequency: Annually or as per utility guidelines.
- Key Tests:
- Insulation Resistance Test (Megger Test): Ensures windings and core are properly insulated.
- Turns Ratio Test: Verifies the correct ratio between primary and secondary windings.
- Winding Resistance Test: Checks for resistance changes that could indicate faults or loose connections.
- Polarity and Phase Test: Confirms correct winding polarity and phase alignment.
5. Cooling System Maintenance
- Frequency: Semi-annually or annually.
- What to Do:
- Clean radiators, fins, and cooling ducts to ensure proper heat dissipation.
- Inspect fans, pumps, and cooling fluid circulation systems for functionality.
- Replace or replenish cooling oil if tests indicate degradation.
6. Tap Changer Maintenance
- Frequency: Annually for off-load, more frequent for on-load tap changers.
- Tasks:
- Clean contacts and replace damaged components.
- Check and lubricate mechanisms.
- Verify proper operation and voltage adjustments.
7. Grounding and Connections
- Frequency: Semi-annually or annually.
- What to Check:
- Tightness of grounding connections.
- Integrity of grounding wires and clamps.
- Inspect and tighten all terminal connections to prevent overheating.
8. Bushing Inspection
- Frequency: Annually.
- What to Check:
- Clean bushings to remove contaminants.
- Inspect for cracks, chips, or signs of arcing.
- Measure capacitance and power factor to detect insulation degradation.
9. Protection Systems
- Frequency: Annually or more frequently if critical.
- What to Check:
- Inspect and test protective relays, fuses, and circuit breakers.
- Verify functionality of temperature and pressure relief devices.
Maintenance Practices for Electrical Devices
1. Circuit Breakers
- Tasks:
- Test tripping mechanisms to ensure proper fault detection.
- Inspect and clean contacts to prevent arcing.
- Verify insulation resistance and check for overheating.
2. Relays
- Tasks:
- Inspect and calibrate relays for accurate operation.
- Test response time and settings to ensure proper functionality.
3. Switchgear
- Tasks:
- Clean and lubricate moving parts.
- Inspect busbars and insulators for signs of corrosion or contamination.
- Conduct insulation resistance and contact resistance tests.
4. Motors
- Tasks:
- Measure insulation resistance and winding temperatures.
- Inspect and lubricate bearings to avoid wear and overheating.
- Clean cooling fans and vents to ensure adequate airflow.
5. Transformers in Appliances
- Tasks:
- Inspect for signs of physical damage or overheating.
- Verify voltage output and connections.
- Replace if degradation or faults are detected.
6. Capacitors
- Tasks:
- Inspect for bulging, leakage, or physical damage.
- Measure capacitance and test insulation resistance.
- Verify proper grounding.
General Maintenance Practices
1. Cleaning
- Keep all electrical devices clean and free of dust, dirt, and moisture.
- Use non-conductive cleaning agents to avoid damage.
2. Tightening Connections
- Check and tighten all electrical connections periodically to prevent overheating due to loose connections.
3. Lubrication
- Regularly lubricate moving parts in switches, relays, and mechanical components.
4. Thermal Scanning
- Use infrared cameras to identify overheating components in electrical systems.
5. Regular Load Testing
- Measure and monitor load conditions to ensure devices are not overloaded.
6. Grounding System Checks
- Inspect and test grounding systems to ensure safe operation and protection against electrical faults.
7. Inspection of Protective Devices
- Test and verify the proper operation of fuses, surge protectors, and circuit breakers.
A robust maintenance schedule for transformers and electrical devices includes regular inspections, testing, cleaning, and repairs. Following these practices ensures reliable performance, reduces downtime, and prevents costly failures. Maintenance frequency should align with manufacturer recommendations, operating conditions, and the criticality of the equipment in the system.